Koronavirus - Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia, ensiklopedia bebas
Encrypting your link and protect the link from viruses, malware, thief, etc! Made your link safe to visit.
Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia, ensiklopedia bebas
Koronavirus [5] atau coronavirus (istilah populer: virus korona, virus corona, atau virus Corona) adalah sekumpulan virus dari subfamili Orthocoronavirinae dalam keluargaCoronaviridae dan ordoNidovirales.[6][7] Kelompok virus ini yang menmemperoleh menyebabkan penyakit pada burung dan mamalia (termasuk manusia).[8] Pada Humanisme, koronavirus menyebabkan infeksi saluran pernapasan yang umumnya ringan, tampaknya pilek, meskipun beberapa bentuk penyakit seperti SARS, MERS, dan COVID-19 sifatnya Hiperbola mematikan. Manifestasi klinis yang muncul cukup beragam pada spesies lain: pada ayam, koronavirus menyebabkan penyakit saluran pernapasan atas, sedangkan pada sapi dan babi menyebabkan diare. Belum ada vaksin atau obat antivirus untuk mencegah atau mengobati infeksi koronavirus pada manusia.
Koronavirus yaitu virus beramplop dengan genomRNA utas tunggal plus dan nukleokapsid berbentuk heliks simetris. Jumlah genom koronavirus berkisar antara 27–34 kilo pasangan basa, terbesar di JumAwang-awang virus RNA yang diketahui.[9] Nama koronavirus asal dari bahasa Latincorona yang artinya mahkota, yang mengacu pada tampilan partikel virus (virion): mereka memiliki pinggiran yang mengingatkan pada mahkota atau korona matahari.
Koronavirus ditemukan pada 1960-an.[10] Virus yang paling awal ditemukan adalah virus bronkitis infeksius pada ayam dan dua virus dari rongga hidung Humanisme dengan flu biasa yang kemudian diberi nama human coronavirus 229E dan human coronavirus OC43.[11] Sejak saat itu, anggota koronavirus yang lain akan diidentifikasi, termasuk SARS-CoV pada 2003, HCoV NL63 pada 2004, HKU1 pada 2005, MERS-CoV (sebelumnya dikenal sebagai 2012-nCoV) pada 2012, dan SARS-CoV-2 (sebelumnya dikenal sebagai 2019-nCoV) pada 2019; sebagian Serebrum dari virus-virus ini terkait dengan infeksi saluran pernapasan yang serius.
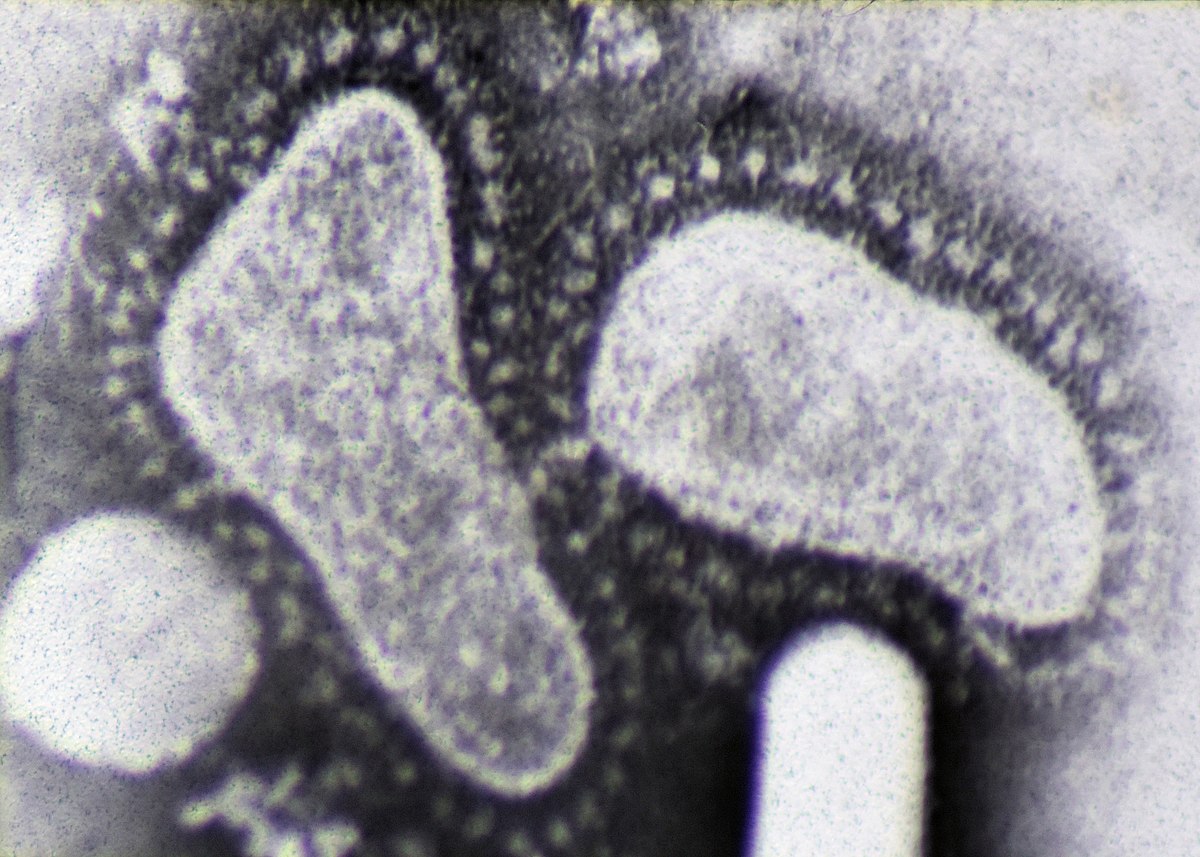
Nama koronavirus asal dari bahasa Latin corona dan bahasa Yunani κορώνη (korṓnē, "lingkaran, untaian"), yang berarti mahkota atau lingkaran cahaya. Namanya mengacu pada penampilan karakteristik virion (bentuk infektif virus) dalam mikroskop elektron, yang memproyeksikan pinggiran permukaan virus yang besar dan Ditenggak yang menghasilkan gambar yang mengingatkan pada mahkota atau korona matahari. Morfologi ini diciptakan oleh peplomer tonjolan protein permukaan virus (S), yang menentukan tropisme inang.
Protein yang menyusun InPelatih koronavirus yaitu protein tonjolan (spike) (S), amplop (E), membran (M), dan nukleokapsid (N). DKI pada virus SARS, letak pengikatan reseptor pada protein S memediasi perlekatan virus ke reseptor sel inangnya merupakan, enzim pengubah angiotensin (ACE2).[12] Beberapa koronavirus (khususnya anggota Betacoronavirus garis keturunan A) juga memiliki tonjolan protein pendek yang disebut hemaglutinin esterase (HE).[6]
Penularan koronavirus dari Humanisme ke manusia diperkirakan terjadi melalui kontak langsung dalam jarak dekat via tetesan kecil atau percikan (droplet) dari saluran pernapasan yang dihasilkan penderita saat bersin dan batuk.[13]
Nama ilmiah buat koronavirus adalah Orthocoronavirinae atau Coronavirinae. Subfamili ini terdiri atas 4 genus, 25 subgenus, dan 45 spesies.[2][14][15]
| Genus | Subgenus | Spesies | Inang |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alphacoronavirus | Colacovirus | Bat coronavirus CDPHE15 | kelelawar |
| Decacovirus | Bat coronavirus HKU10 | kelelawar | |
| Rhinolophus ferrumequinum alphacoronavirus HuB-2013 | kelelawar | ||
| Duvinacovirus | Humanisme coronavirus 229E | manusia, kelelawar, unta | |
| Luchacovirus | Lucheng Rn rat coronavirus | rodensia | |
| Minacovirus | Mink coronavirus 1 | mink, ferret | |
| Minunacovirus | Miniopterus bat coronavirus 1 | kelelawar | |
| Miniopterus bat coronavirus HKU8 | kelelawar | ||
| Myotacovirus | Myotis ricketti alphacoronavirus Sax-2011 | kelelawar | |
| Nyctacovirus | Nyctalus velutinus alphacoronavirus SC-2013 | kelelawar | |
| Pipistrellus kuhlii coronavirus 3398 | kelelawar | ||
| Pedacovirus | Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus | babi | |
| Scotophilus bat coronavirus 512 | kelelawar | ||
| Rhinacovirus | Rhinolophus bat coronavirus HKU2 | kelelawar | |
| Setracovirus | Humanisme coronavirus NL63 | manusia | |
| NL63-related bat coronavirus strain BtKYNL63-9b | kelelawar | ||
| Soracovirus | Sorex araneus coronavirus T14 | celurut | |
| Sunacovirus | Suncus murinus coronavirus X74 | celurut | |
| Tegacovirus | Alphacoronavirus 1 | anjing, kucing, babi | |
| Betacoronavirus | Embecovirus | Betacoronavirus 1 | manusia, sapi, kuda, babi |
| China Rattus coronavirus HKU24 | rodensia | ||
| Humanisme coronavirus HKU1 | manusia | ||
| Murine coronavirus | rodensia | ||
| Myodes coronavirus 2JL14 | vole | ||
| Hibecovirus | Bat Hp-betacoronavirus Zhejiang2013 | kelelawar | |
| Merbecovirus | Hedgehog coronavirus 1 | landak susu | |
| Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus | manusia, unta | ||
| Pipistrellus bat coronavirus HKU5 | kelelawar | ||
| Tylonycteris bat coronavirus HKU4 | kelelawar | ||
| Nobecovirus | Eidolon bat coronavirus C704 | kelelawar | |
| Rousettus bat coronavirus GCCDC1 | kelelawar | ||
| Rousettus bat coronavirus HKU9 | kelelawar | ||
| Sarbecovirus | Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus | manusia, kelelawar, tenggiling, Viverridae, Canidae, Felidae | |
| Gammacoronavirus | Brangacovirus | Goose coronavirus CB17 | itik |
| Cegacovirus | Beluga whale coronavirus SW1 | paus | |
| Igacovirus | Avian coronavirus | burung | |
| Avian coronavirus 9203 | burung | ||
| Duck coronavirus 2714 | itik | ||
| Deltacoronavirus | Andecovirus | Wigeon coronavirus HKU20 | burung |
| Buldecovirus | Bulbul coronavirus HKU11 | burung | |
| Common moorhen coronavirus HKU21 | burung | ||
| Coronavirus HKU15 | babi | ||
| Munia coronavirus HKU13 | burung | ||
| White-eye coronavirus HKU16 | burung | ||
| Herdecovirus | Night heron coronavirus HKU19 | burung |
Koronavirus diyakini menyebabkan 15–30% dari seluruh pilek pada orang dewasa dan anak-anak.[16] Koronavirus menyebabkan pilek Herbi gejala utama seperti demam dan sakit tenggorokan akibat pembengkakan adenoid, terutama pada musim dingin dan awal musim semi.[17] Koronavirus menmemperoleh menyebabkan pneumonia, baik pneumonia virus langsung atau pneumonia bakterial sekunder, dan dapat menyebabkan bronkitis, baik bronkitis virus langsung atau bronkitis bakterial sekunder.[18] Koronavirus Humanisme yang ditemukan pada tahun 2003, SARS-CoV, yang menyebabkan sindrom pernafasan akut berat (SARS), memiliki patogenesis yang unik karena menyebabkan infeksi saluran pernapasan bagian atas dan bawah.[18] Tentatif ada vaksin atau obat antivirus untuk mencegah atau mengobati infeksi koronavirus manusia.[19]
Tujuh galur koronavirus Humanisme yang saat ini diketahui:
- Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E)
- Humanisme coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43)
- Koronavirus sindrom pernapasan akut berat (SARS-CoV)
- Humanisme coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63, New Haven coronavirus)
- Humanisme coronavirus HKU1
- Koronavirus terkait sindrom pernafasan Timur Tengah (MERS-CoV), yang sebelumnya dikenal sebagai novel coronavirus 2012 dan HCoV-EMC
- Koronavirus sindrom pernapasan akut berat 2 (SARS-CoV-2), sebelumnya dikenal sebagai 2019-nCoV atau "novel coronavirus 2019"
Koronavirus HCoV-229E, -NL63, -OC43, dan -HKU1 terus beredar dalam populasi Humanisme dan menyebabkan infeksi pernapasan pada orang dewasa dan anak-anak di semua dunia.[20]
Beberapa wabah koronavirus dengan mortalitas yang relatif tinggi adalah sebagai berikut:
- ^ "2017012-015S". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) (dalam bahasa Inggris). October 2018. Diarsipkan dari versi asli(xlsx) tanggal 14 May 2019. Diakses tanggal 24 January 2020.
-
^
Fan Y, Zhao K, Shi ZL, Zhou P (March 2019). "Bat Coronaviruses in China". Viruses. 11 (3): 210. doi:103390/v11030210. PMC 6466186
 . PMID 30832341.
. PMID 30832341.
- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2018b Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) (dalam bahasa Inggris). March 2019. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 4 March 2018. Diakses tanggal 24 January 2020.
- ^ ab de Groot RJ, Baker SC, Baric R, Enjuanes L, Gorbalenya AE, Holmes KV, Perlman S, Poon L, Rottier PJ, Talbot PJ, Woo PC, Ziebuhr J (2011). "Family Coronaviridae". Dalam King AM, Lefkowitz E, Adams MJ, Carstens EB, International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, International Union of Microbiological Societies. Virology Division. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Oxford: Elsevier. hlm. 806–828. ISBN 978-0-12-384684-6.
- ^ International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (24 Agustus 2010). "ICTV Master Species List 2009 – v10"(xls).
- ^ (Inggris) Wolfgang B. Fischer (2005). Viral membrane proteins: structure, function, and drug design. Springer. ISBN 978-0-306-48495-7. Page.49-52
-
^
Sexton NR, Smith EC, Blanc H, Vignuzzi M, Peersen OB, Denison MR (Agustus 2016). "Homology-Based Identification of a Mutation in the Coronavirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase That Confers Resistance to Multiple Mutagens". Journal of Virology. 90 (16): 7415–7428. doi:10.1128/JVI.00080-16. PMC 4984655
 . PMID 27279608.
. PMID 27279608. CoVs also have the largest known RNA virus genomes, ranging from 27 to 34 kb (31, 32), and increased fidelity in CoVs is likely required for the maintenance of these large genomes (14).
- ^ "Coronavirus: Common Symptoms, Preventive Measures, & How to Diagnose It". Caringly Yours (dalam bahasa Inggris). 2020-01-28. Diakses tanggal 28 Januari 2020. [pranala nonaktif permanen]
-
^
Geller C, Varbanov M, Duval RE (November 2012). "Human coronaviruses: insights into environmental resistance and its influence on the development of new antiseptic strategies". Viruses. 4 (11): 3044–68. doi:10.3390/v4113044. PMC 3509683
 . PMID 23202515.
. PMID 23202515.
- ^ Li F, Li W, Farzan M, Harrison SC (September 2005). "Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain complexed with receptor". Science. 309 (5742): 1864–8. Bibcode:2005Sci...309.1864L. doi:10.1126/science.1116480. PMID 16166518.
- ^ "Transmission of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) | CDC". www.cdc.gov (dalam bahasa Inggris). 2020-01-31. Diakses tanggal 1 Februari 2020.
- ^ ICTV (2020). "Taxonomy". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) (dalam bahasa Inggris). Diakses tanggal 22 Mei 2021.
- ^ Zhou, Zhijian; Qiu, Ye; Ge, Xingyi (April 2021). "The taxonomy, host range and pathogenicity of coronaviruses and other viruses in the Nidovirales order". Animal Diseases. 1 (1): 5. doi:10.1186/s44149-021-00005-9. ISSN 2731-0442.
-
^
Fehr AR, Perlman S (2015). "Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis". Methods in Molecular Biology. 1282: 1–23. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1. ISBN 978-1-4939-2437-0. PMC 4369385
 . PMID 25720466.
. PMID 25720466.
-
^
Liu P, Shi L, Zhang W, He J, Liu C, Zhao C, et al. (November 2017). "Prevalence and genetic diversity analysis of human coronaviruses among cross-border children". Virology Journal (dalam bahasa Inggris). 14 (1): 230. doi:101186/s12985-017-0896-0. PMC 5700739
 . PMID 29166910.
. PMID 29166910.
- ^ ab Forgie S, Marrie TJ (February 2009). "Healthcare-associated atypical pneumonia". Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 30 (1): 67–85. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1119811. PMID 19199189.
- ^ Habibzadeh P, Stoneman EK (February 2020). "The Novel Coronavirus: A Bird's Eye View". The International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 11 (2): 65–71. doi:10.15171/ijoem.2020.1921. PMID 32020915.
- ^ Corman VM, Muth D, Niemeyer D, Drosten C (2018). "Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses". Advances in Virus Research. 100: 163–188. doi:10.1016/bs.aivir.2018.01.001. ISBN 978-0-12-815201-0. PMID 29551135.
- ^ Smith RD (Desember 2006). "Responding to global infectious disease outbreaks: lessons from SARS on the role of risk perception, communication and management". Social Science & Medicine. 63 (12): 3113–23. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2006.08.004. PMID 16978751.
- ^ "Case‐control study to assess potential risk factors related to human illness caused by the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)" (PDF). World Health Organization. 28 Maret 2014. Diakses tanggal 24 April 2014.
- ^ "Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – Republic of Korea". World Health Organization (dalam bahasa Inggris). Diakses tanggal 1 Desember 2016.
- ^ Pandemic Epidemic Diseases news: Infectious disease outbreaks reported in the Eastern Mediterranean region in 2018 Diarsipkan 29 January 2020 di Wayback Machine. Between 12 January through 31 May 2018, the National IHR Focal Point of The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia reported 75 laboratory confirmed cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS_CoV), including twenty-three (23) deaths. Date www.emro.who.int, accessed 29 January 2020
- ^ "COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU)". ArcGIS. Johns Hopkins University. Diakses tanggal 1 November 2021.
Sincery dab.us
SRC: https://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/Koronavirus





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Koronavirus - Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia, ensiklopedia bebas"
Posting Komentar